Missouri Botanical Yard scientists had been amongst a world evaluation workers that used 1.8 billion letters of genetic code to assemble groundbreaking tree of life.
A paper printed this spring throughout the journal Nature shares most likely probably the most up-to-date understanding of the flowering plant tree of life.
“That’s the outcomes of a major worldwide collaborative effort aimed towards understanding relationships amongst flowering vegetation,” acknowledged Yard Scientist Mónica Carlsen.

What’s a tree of life?
Sometimes often called a “periodic desk for flowering vegetation,” the tree of life is a tool that biologists use to map how organisms are related.
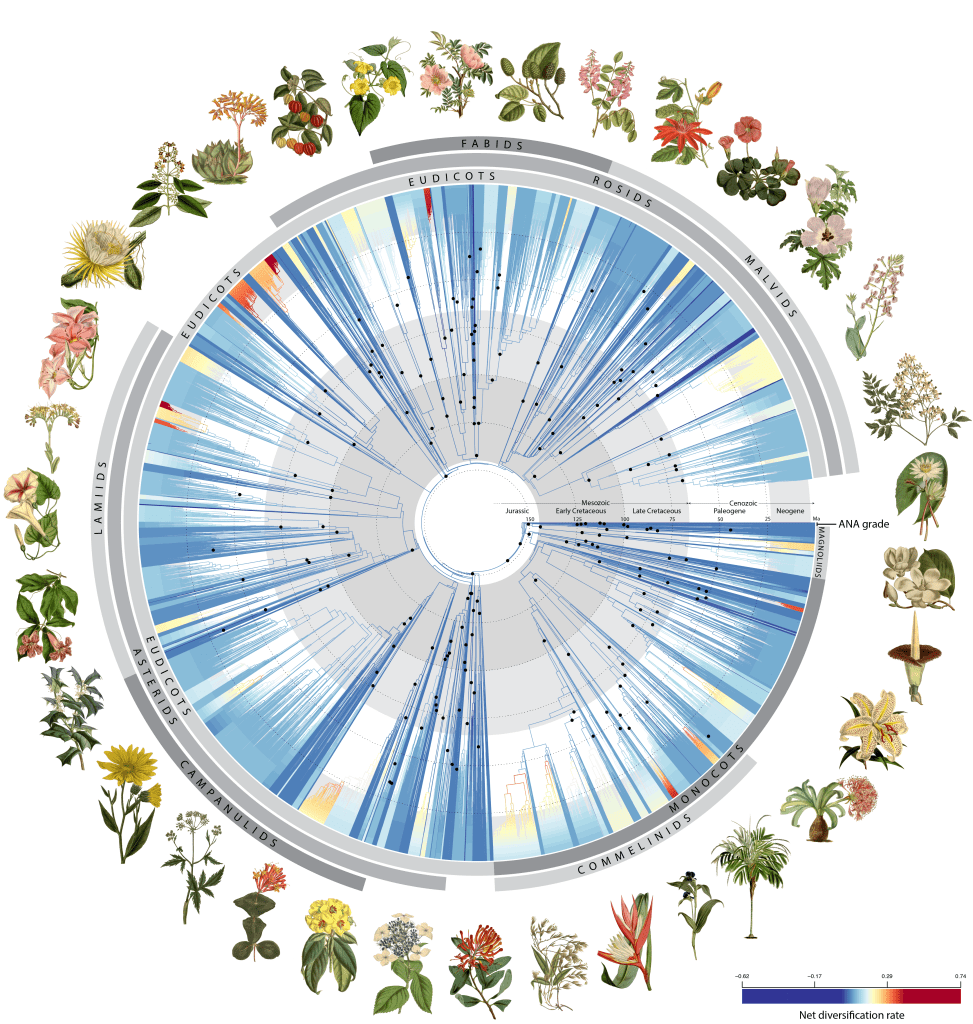
Developing the tree of life
Using 1.8 billion letters of genetic code from better than 9,500 species overlaying almost 8,000 acknowledged flowering plant genera, this unimaginable achievement sheds new mild on the evolutionary historic previous of flowering vegetation and their rise to ecological dominance on Earth. The analysis’s authors think about the knowledge will help future makes an try to determine new species, refine plant classification, uncover new medicinal compounds, and protect vegetation throughout the face of native climate change and biodiversity loss.
“Understanding how the very good number of flowering vegetation we see in our planet have originated and what variety of 1000’s and 1000’s of years it took to evolve, makes us actually really feel additional deeply associated with nature and locations in perspective the importance of worldwide plant conservation for all,” acknowledged Carlsen.

Major Milestone
The Yard is amongst 138 worldwide organizations that contribute to the milestone enterprise that constructed on 15 situations additional information than any comparable analysis of the flowering plant tree of life.
Among the many many species sequenced for this analysis, better than 800 have not at all had their DNA sequenced sooner than along with six samples equipped by Carlsen. The sheer amount of knowledge unlocked by this evaluation, which could take a single laptop 18 years to course of, is an enormous stride in route of developing a tree of life for all 330,000 acknowledged species of flowering vegetation – an unlimited endeavor by Kew’s Tree of Life Initiative.

Why the tree of life points
The flowering plant tree of life, similar to our household tree, permits us to know how utterly totally different species are related to at least one one other. Scientists uncover the tree of life by evaluating DNA sequences between utterly totally different species to determine changes (mutations) that accumulate over time like a molecular fossil file. Our understanding of the tree of life is enhancing shortly in tandem with advances in DNA sequencing know-how. For this analysis, scientists developed new genomic methods to magnetically seize an entire bunch of genes and an entire bunch of 1000’s of fashions of genetic code from every sample, orders of magnitude better than earlier methods.
“The flowering plant tree of life has enormous potential in biodiversity evaluation,” Carlsen outlined. “Merely as one can predict the properties of a part primarily based totally on its place throughout the periodic desk, the position of a species throughout the tree of life permits us to predict its properties. This new information shall be invaluable for enhancing many areas of science and previous.”

The place did scientists get the DNA?
The evaluation workers used a big number of plant supplies, outdated and new, to be sequenced. Even when the DNA is badly damaged, the workers can nonetheless use it.
Herbaria
One key provide for accumulating DNA was from the world’s herbarium collections – collections of dried plant specimens – that comprise virtually 400 million scientific specimens of vegetation.
All through all 9,506 species sequenced, over 3,400 received right here from supplies sourced from 163 herbaria in 48 worldwide places.

The Missouri Botanical Yard has certainly one of many largest herbaria on this planet, with better than 7.5 million specimens. Dozens of samples for the enterprise received right here from the Yard’s Herbarium, along with unusual species with restricted geographic ranges not acknowledged from dwelling collections. Bognera recondita, a genus throughout the aroid family comprising solely a single species, for instance, found solely in distant areas of Amazonian Brazil near the Peruvian border. Its establish means “hidden.’
“Herbaria are essential property for the analysis of the world’s vegetation, notably when these vegetation develop in areas which is perhaps robust or dangerous to entry,” acknowledged Yard Herbarium Director Jordan Teisher. “A stroll by the aisles of the Herbarium is like being able to teleport all through continents, from the slopes of the Andes to the deep forests of the Congo or distant islands of Indonesia.”
World plant collections
Additional supplies from plant collections all around the world, whether or not or not in DNA banks, seeds, or dwelling collections, had been moreover essential for filling key information gaps to shed new mild on the historic previous of flowering plant evolution. The workers moreover benefited from publicly accessible information for over 1,900 species, highlighting value of the open science technique to future genomic evaluation.

Fixing a Centuries’ Outdated Thriller
Flowering vegetation alone account for about 90% of all acknowledged flowers on land and are almost everywhere on the planet. However, our understanding of how these vegetation received right here to dominate the scene shortly after their origin has baffled scientists for generations, along with Charles Darwin. Flowering vegetation originated better than 140 million years prior to now after which they shortly overtook totally different vascular vegetation along with their closest dwelling kinfolk – the gymnosperms (non-flowering vegetation which have naked seeds, similar to cycads, conifers, and ginkgo). Darwin was mystified by the seemingly sudden look of such selection throughout the fossil file.
For his or her evaluation, the scientists used 200 fossils to see how flowering vegetation developed all through geological time. They found that early flowering vegetation did actually explode in selection, giving rise to over 80% of the foremost lineages that exist at the moment shortly after their origin. Nonetheless, this growth then declined to a steadier worth for the next 100 million years until one different surge in diversification about 40 million years prior to now, coinciding with a worldwide decline in temperatures.

Working Globally, Open Entry
In entire, 279 authors had been contributed to the evaluation, representing many different nationalities from 138 organizations in 27 worldwide places. Worldwide collaborators moreover shared their distinctive botanical expertise, along with many treasured plant samples from all around the world. 5 Yard scientists are among the many many coauthors. They equipped samples from the Yard’s collections and shared their expertise in species identification and taxonomy.
Due to these shared efforts, the tree and all of the information that underpin it are openly and freely accessible to every most of the people and scientific group, along with by the Kew Tree of Life Explorer. The analysis’s authors think about such open entry is important to democratizing entry to scientific information all through the globe.
“Open entry makes it attainable for additional scientists, protection makers, practitioners, and most people to have the power to view, cite, re-use and share this work along with its potential benefits,” acknowledged Carlsen.